Forging
Under the influence of impact or pressure forces, a controlled plastic shaping process of the part with the help of a mold, usually as hot, semi-hot or cold, is called forging. It is one of the oldest production methods (forged sword production) with a history of 4000 years.
According to Temperature;
According to Mold Type;
- Open die forging
- Closed die forging
Forging Types
Hot Forging
The forging is heated to a lower temperature of the molten phase (one below the liquid phase). Parts can be forged with less force.
But,
- part dimensions cannot be obtained with sufficient precision,
- large and rough parts are beaten more easily this way,
- surface roughness is not good,
- contains oxide on the surface,
Cold Forging
The part to be forged is required to be ductile. The part is heated to the desired temperature (without the solid form deteriorating). It is a form of production that requires more power.
- part dimensions can be obtained with sufficient precision,
- medium and small sized pieces are beaten more easily this way,
- Surface roughness and quality are good,
- does not contain oxide on the surface,
- is a method open to mass production,
Open Die Forging
Simple, coarsely shaped parts are forged. It is a type of hot forging. They are processes in which cylindrical, rectangular or prism parts are forged.
The open mold continues the determined number of pressing/strokes throughout the process until it reaches the part dimensions. This process can also be done by placing several different molds in succession.
Closed Die Forging
It is a type of hot forging. The annealed piece is placed between the male and female mold. Under high power, plastic deformation of the part is achieved. It is generally a form of burr production. The part is then deburred and heat treated.
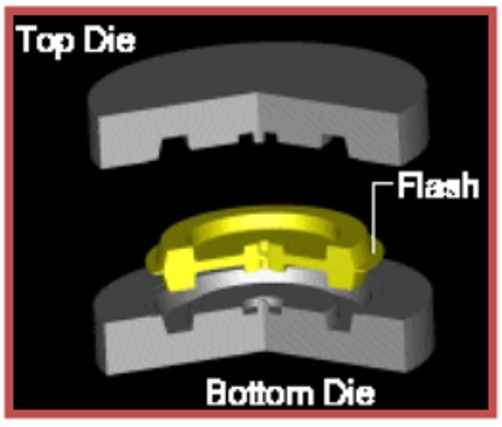
- Suitable for mass production,
- Quality control costs are low,
- with measurement precision,
- Good surface quality
- Difficult to form/shape,
- It is an ideal production method for parts with high mechanical strength.
Aluminum Alloys and Forging
Due to its alloy diversity, forging and post-forging machining capability, corrosion ability, coating and paint capability, and most importantly, its lightness, it has quickly taken its place in industrial applications in recent years as a substitute for steel forging products. Although all alloys are suitable for the forging process, in industrial applications generally; 2XXX, 6XXX and 7XXX series are used.
Forged products made of aluminum alloys; It has started to be used in almost all sectors, especially in aerospace, defense, automotive, marine, rail systems, general machinery / mold, electricity / electromechanical / energy, tanker / bulk truck, pressure tube and health / medical sectors.
Our Forging Capabilities
Technical Support and Experience of Aluminium and Forging

All kinds of technical and engineering support on the basis of the sector, especially the material selection related to the product, are provided by our company personnel.
Our company employs 14 Engineers in different branches, mainly Metallurgical and Materials Science Engineers.
In order for our customers to reach more accurate and up-to-date information in their sectors, the necessary training activities are given to them visually and practically in our company.
Design/R&D/Innovation

With Simufact software, "Forging Simulation" of designed products is performed. Thus, risks are determined and necessary corrections are made before the part is even in the production phase. In this way; product costs are reduced and sample product production time is shortened.
Thus, it is possible to deliver quality products to the customer in a shorter time.
High-Tech Machine Park

One of the ways to provide the best service to our customers is to follow the technological developments and to strengthen our machinery by providing the latest technology equipment required by our production.
In this context, our facility has equipment, the main details of which are given below:
- Automatic Cutting Saws,
- Forging Presses From 100 Tons To 2.500 Tons,
- Horizontal Cold Drawing Presses,
- Heat Treatment Facilities,
- CNC Router, (Cutting, Drilling, Scraping and Forming)
- CNC / Universal Machining Machines, (Turning, Milling, Drill, etc.)